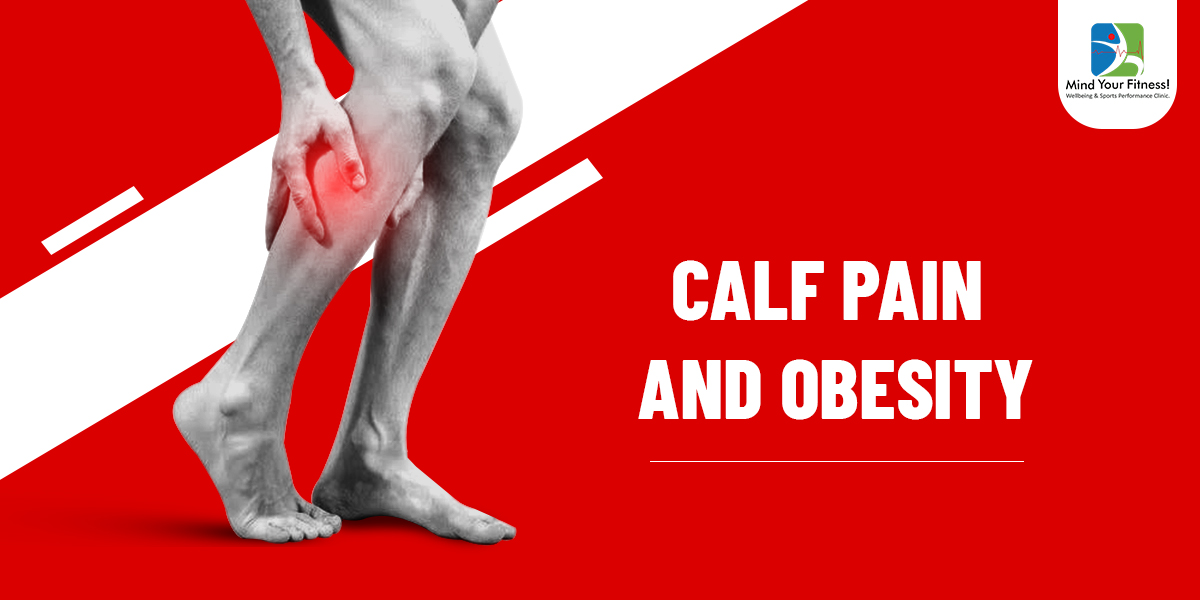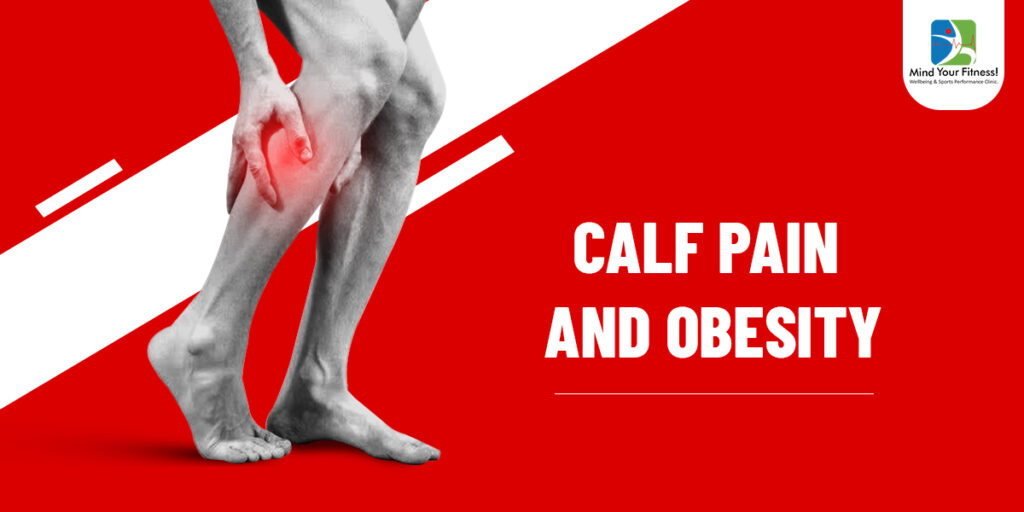
Calf muscle is an anti-gravity muscle and helps in walking/ running/ jogging/ sprinting/static standing posture.
Skeletal muscle pump: the calf muscle also helps in pumping blood back to the heart through the venous system through the dorsiflexion & plantar flexion movements of the ankle,thereby causing significant calf muscle contraction.
The strength & flexibility of calf muscle plays a vital role to maintain an efficient skeletal muscle pump action.
Causes of pain:
- Prolonged standing.
- Overuse of calf muscle eg: running/sprinting, ankle sprain.
- Lack of exercises for leg muscles.
- Lack of calf stretching routine in exercising individuals.
- Deficiencies eg: Vit D/calcium.
- Foot and ankle dysfunction , eg: Flat feet / High arched foot alignment.
- Varicose veins in the calf muscles.
- Obesity.
- Dehydration.
- Blood clots or Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT).
Calf pain & Obesity:
- Obese individuals are prone to calf pain if there is lack of exercise , which leads to reduced strength & increased tightness of the calf muscle.
- Tightness in the calf muscle can be responsible for cramps or dull aching calf pain and therefore a mechanical stress on the deep blood vessels located in the calf muscle.
- Sudden increase in activity without a proper exercise regime in obese people can lead to calf muscle strains.
- If there is swelling around the foot and ankle in an obese person, this makes it difficult to wear proper-fitting shoes. This is a major cause for ankle-foot imbalances.
- Mechanical stress can lead to adult-acquired flat foot or ankle over-pronation, this malalignment leads to leg and calf pain.
- Obese individuals may also have metabolic issues like diabetes which can lead to peripheral artery disease and obstruction of blood flow in the legs.
Dr. Janhvi Vayada – Clinical Sports Physiotherapist